그래프 탐색 알고리즘 BFS/DFS
09 Jul 2021 | TILBFS, DFS의 5분 설명 및 코드화
DFS 코드
__author__ = 'Minsuk Heo'
vertexList = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6']
edgeList = [(0,1), (0,2), (1,0) , (1,3) , (2,0) , (2,4) , (2,5) , (3,1), (4,2) , (4,6), (5,2), (6,4)]
#각 번호별로 인접한 번호가 무엇이 있는지 리스트로 저장
graphs = (vertexList, edgeList)
def dfs(graph, start):
vertexList, edgeList = graph
visitedVertex = []
stack = [start]
#스택을 하나 준비해주세요, stack에 0을 집어넣으면 while 루프가 실행이 됩니다..?
adjacencyList = [[] for vertex in vertexList]
#인접 리스트 생성
for edge in edgeList:
adjacencyList[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
# adjacencyList :
#[
# [1,2] // vertex 0
# [0,3] // vertex 1
# [0,4,5] // vertex 2
# [1] // vertex 3
# [2,6] // vertex 4
# [2] // vertex 5
# [4] // vertex 6
#]
while stack:
current = stack.pop()
# 0이 스택을 거쳐 커렌트에 들어간다
for neighbor in adjacencyList[current]:
# 커렌트에 들어있는 0의 이웃들 중에서
if not neighbor in visitedVertex:
# 이미방문한숫자 리스트에 들어있지 않다면
stack.append(neighbor)
# 0의 이웃인 1과 2가 스택에 들어간다
visitedVertex.append(current)
#이미방문한숫자 리스트에 커렌트에 있는 0을 넣어준다
return visitedVertex
print(dfs(graphs, 0))
BFS(너비우선탐색)와 DFS(깊이우선탐색)의 차이
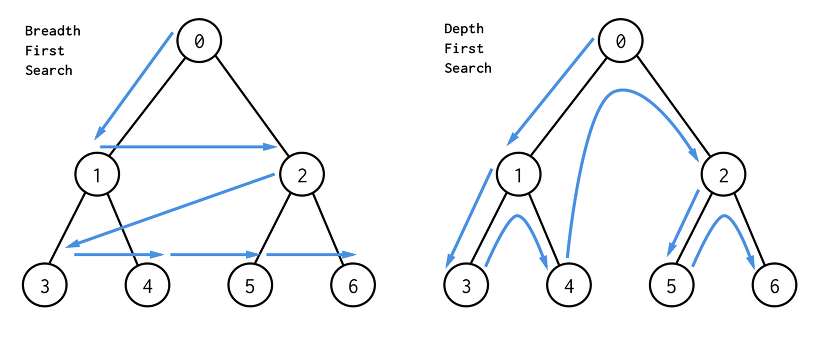
BFS 코드
__author__ = 'Minsuk Heo'
vertexList = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G']
edgeList = [(0,1), (1,2), (1,3), (3,4), (4,5), (1,6)]
graphs = (vertexList, edgeList)
def bfs(graph, start):
vertexList, edgeList = graph
visitedList = []
queue = [start]
adjacencyList = [[] for vertex in vertexList]
# fill adjacencyList from graph
for edge in edgeList:
adjacencyList[edge[0]].append(edge[1])
# bfs
while queue:
current = queue.pop()
for neighbor in adjacencyList[current]:
if not neighbor in visitedList:
queue.insert(0,neighbor)
visitedList.append(current)
return visitedList
print(bfs(graphs, 0))
주요 포인트 및 생각해볼 점
자료구조의 개요
1)선형 구조
- 배열, 연결 리스트, 스택, 큐
2)비선형 구조
- 트리, 그래프
트리와 그래프에 대해서 더 공부해봐야겠다! - 2021.10.21
자료구조 인강을 다시 들어봐야겠다. 초보몽키 블로그 - 강의노트 17. 알고리즘, 자료구조 개요
